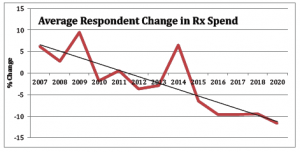
The work comp Pharmacy Benefit Management business has become hyper-competitive; total drug spend has dropped 6 of the last 7 years, there’s been massive consolidation of PBMs, margins are declining…all signs of a very mature industry.
Sounds like a not-very-attractive-business…right?
Well, due to accounting rules, PBMs are still wildly popular among work comp service companies.
They love PBMs because the companies get to count the cost of the drugs as well as their margins as top-line revenues – which makes those service companies look bigger than they really are.
The problem is…once you buy a PBM, you get a big one-time increase in revenue. But – and it’s a BIG but, unless you figure out how to grow that PBM revenue in a business that is declining, your top line flat-lines.
If you’re looking to sell your work comp service company, or otherwise tout strong financial performance, that is not a good look. Which brings me to a creative way a PBM is generating script volume without adding new payer customers.
Occ med clinic giant Concentra’s providers are writing scripts that direct the pharmacy filling the script to send it to Mitchell Pharmacy Solutions for administration. (I looked for a company link, but couldn’t locate any mention of Concentra’s OccuScript program on their website)
According to Concentra, the OccuScript program:
- has been in place for quite some time;
- is mostly – but by no means exclusively – used in states where physician dispensing is not allowed (e.g. Texas);
- appears to primarily address initial prescription fills which are mostly generics prescribed for a limited time;
- about one of every nine scripts written in the company’s 520 clinics and 120 onsite centers flows through the program. Mitchell is the current administrator, providing network access and the claim adjudication platform. To be clear, Mitchell does not use its own pharmacy network…they contract with Script Care.

Injured workers treated at this clinic may be – or more likely are not – covered by a payer that contracts with Mitchell. (Mitchell is one of several work comp PBMs – and far from the largest.) If it’s a Mitchell-contracted payer this form/process is helpful indeed.
In an email conversation with Concentra, the company noted “OccuScript supports medication compliance which is fundamental to evidence-based care delivery and positive patient outcomes.” (note Concentra stated in an email “We have national employer customers whose injured workers are never processed through the OccuScript program…(some payers instruct Concentra on how to process scripts for their injured workers.))
Medication compliance is important indeed, but there are several potential issues/concerns/problems if the injured worker is NOT covered by a Mitchell-contracted payer.
- The payer gets a bill from a non-contracted billing entity which adds a lot of work for claims adjusters who have to figure out what to do with it.
- Unlike scripts processed by the PBM contracted by the injured worker’s employer/insurer/TPA, the payer finds out about the script AFTER it is dispensed. The drug(s) actually dispensed may – or may not – be:
- duplicates of other scripts,
- contra-indicated due to other drugs prescribed for the injured worker (while prescribers are supposed to ask about other meds, many patients aren’t able to recall drugs they are taking), and/or
- an expensive version of the prescribed drug (there are literally dozens of companies making ibuprofen, many at different prices for the same pill; contracted PBMs control for this with MAC lists.)
- The injured worker’s payer/employer/insurer is usually billed at a rate that is higher than their contracted PBM price – sometimes MUCH higher…driving up the employer’s/insurer’s/taxpayer’s work comp costs.
- Concentra’s OccuScript contracts with Mitchell who in turn contracts with Script Care…
- all of whom have to get paid,
- and adding communication challenges as issues have to pass through several entities.
So what to do?
Concentra avers it is ready and willing to work with payers and employers to route scripts to their PBM. It is also interested in working with PBMs. Sure, most “first fills” are “one and done”…but many are not. Getting on the claim as quickly as possible is an industry-wide best practice.
Note – Concentra execs were quite responsive to my queries about the program; kudos to CEO Keith Newton and Charles Bavier – who runs Concentra’s OccuScript program – for jumping on this.
What does this mean for you?
If you aren’t a Mitchell Pharmacy Solutions customer, get with Concentra ASAP to get those scripts routed to your PBM.
For those unfamiliar with this space…Insurers and TPAs hire Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) to ensure injured workers get the medications they need to recover and return to work. PBMs contract with pharmacies, operate call centers and employ pharmacists – all in an effort to deliver the right drug at the lowest possible price.


 As employment, payroll, and injury rates all remain under pressure, total premiums will remain significantly lower than we’d expect in a non-COVID, non-recession environment. We are also on the tail end of the
As employment, payroll, and injury rates all remain under pressure, total premiums will remain significantly lower than we’d expect in a non-COVID, non-recession environment. We are also on the tail end of the